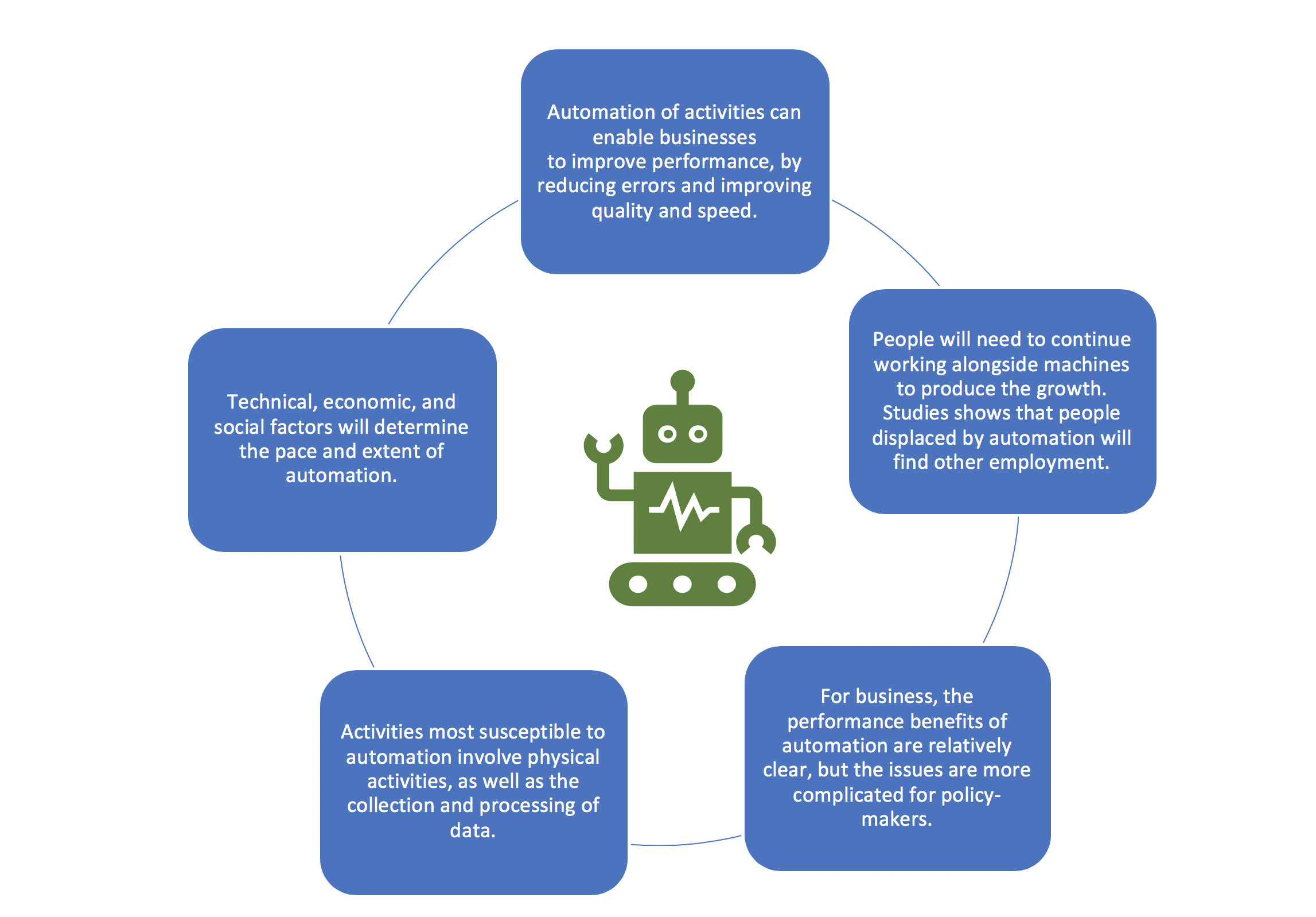
The impact of AI on the labor market is a hotly debated topic, highlighting how artificial intelligence is reshaping the workforce landscape. Recent studies, including the one by Harvard economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers, suggest that technological labor disruption is already underway, leading to significant changes in job market trends. One notable finding is the rise in occupational churn, a phenomenon where job roles and requirements swiftly evolve due to advances in AI and automation. Moreover, the growth in STEM job roles indicates a shift towards employment that necessitates higher skills and training, thus redefining the future workforce. As companies increasingly invest in AI technologies, understanding the implications of these shifts becomes essential for navigating career paths in the modern economy.
Artificial intelligence’s influence on the workforce is becoming increasingly apparent, leading to discussions around the future of employment. This phenomenon, sometimes referred to as technology-induced labor disruption, signifies a transformation in job roles and opportunities across various sectors. The concept of occupational churn illustrates how frequently job categorizations change as new technologies emerge. Trends in the contemporary job market highlight a surge in demand for positions in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM), reflecting a broader shift in labor skills. As the job landscape evolves, it is crucial for professionals to adapt and prepare for the forthcoming challenges and opportunities brought about by advancements in AI.
The Historical Context of Technology and Labor Market Disruption
The labor market has a long history of transformation driven by technological advancement. Over the past century, research highlights how innovations like electricity and the internet have reshaped professions across the board. Economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers emphasize the concept of “occupational churn”, which reflects the changes in employment shares across various sectors, illustrating that while certain jobs may falter, others rise to prominence. This historical context illustrates that the relationship between technology and labor is not a new phenomenon; rather, we are witnessing a continued evolution driven by the rapid adoption of new tools and systems.
As we look back at the past 100 years, periods of stability have surprisingly contrasted with current anxieties regarding AI. Between 1990 and 2017, many people believed that technological advancements would lead to significant job loss; however, data shows that the labor market maintained relatively low churn. This observation is crucial in understanding how previous technological upheavals influenced labor dynamics without immediate drastic unemployment. Instead, cycles of job creation and destruction tend to align with broader economic trends, setting the stage for the next wave of innovation-driven disruption.
AI’s Impact on Labor Market Trends
AI technology is now at the forefront of labor market transformation, illustrating significant shifts in job distribution and employee skill requirements. The study by Deming and Summers indicates that we may be witnessing a resurgence in high-skilled job categories, particularly in STEM fields. As AI and related technological applications become ubiquitous, the demand for workers proficient in these areas is climbing, leading to substantial growth in opportunities for engineers, data scientists, and technology specialists. This shift marks a pivotal change, as high-wage roles expand to meet the emerging needs of the tech-centered economy.
However, AI’s influence on job markets extends beyond just creating new roles. Automation is also driving a decline in many low-wage sectors, reflecting a trend that may reshape the entire workforce landscape. As machines and algorithms take over routine tasks, there is a growing apprehension that a significant number of current roles may dissipate, particularly in retail and low-skilled services. This phenomenon of technology labor disruption underscores the need for a proactive approach from workers to reskill and adapt to the changing dynamics of the job market.
Job Polarization and Its Economic Implications
The phenomenon of job polarization refers to the increasing divide in wage prospects within the labor market. The research reveals that while there has been a significant influx of low-paid jobs, higher-skilled positions have started to flourish as investments in education and training ramp up. However, this dynamic raises concerns regarding economic inequalities, as those without access to upskilling opportunities risk falling behind. Moreover, as AI advancements push industries towards greater reliance on technological solutions, the labor market must grapple with how to integrate a diverse workforce in light of ongoing changes.
This trend towards job polarization not only highlights a shift in the types of roles available but also prompts a reconsideration of policy frameworks. As the labor market bifurcates, there is a pressing need for educational institutions and governments to collaborate in addressing these disparities. Education systems must evolve to meet the rising demand for STEM careers while ensuring that access to quality training is available to all demographics. The implications of job polarization on social fabric cannot be understated, necessitating a concerted effort to ensure an inclusive transition into the future workforce.
Trends in STEM Job Growth Amidst Technological Change
The resurgence in STEM fields represents a vital shift that aligns closely with the ongoing technological evolution. The findings of the study reveal that STEM job share has surged significantly since 2010, increasing from 6.5% to nearly 10% of the job market by 2024. This growth underscores the critical role that technology plays in shaping future employment landscapes, particularly as industries experience increasing demands for innovation and technical expertise. Companies are actively seeking individuals with a strong foundation in scientific and mathematical principles, as these skills are becoming indispensable in navigating the complexities of modern business.
As organizations continue to ramp up investments in AI and other high-tech solutions, the demand for roles centered on technology-related work is expected to rise exponentially. This trend suggests not only a renewed focus on preparation for high-skill roles but also highlights the urgency of fostering interest in STEM education at earlier stages in life. Encouraging young people to pursue studies in science and technology will be paramount to maintaining a competitive workforce that can leverage the advantages of artificial intelligence, ensuring that both individuals and firms can thrive in an increasingly digitized economy.
The Role of Automation Anxiety in the Modern Workforce
Automation anxiety refers to the psychological apprehension many workers feel toward the increasing capabilities of machines and AI systems. Many employees express fears regarding job security as they anticipate potential displacement caused by emerging technologies. This sentiment was particularly pronounced during the early 2000s, with studies indicating nearly 47% of U.S. occupations were at risk of replacement by computers. The correlation between anxiety and the current transformation of the labor market underscores the need for systematic approaches to address worker concerns while embracing the benefits that technology brings.
To mitigate the effects of automation anxiety, it is essential for organizations to cultivate a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. As the labor market evolves, employees must be equipped with the skills to work alongside AI systems rather than fear their presence. Transparent communication from employers about the implications of technology and the commitment to reskilling opportunities can help ease anxiety and foster a more confident workforce. Ultimately, addressing automation anxiety proactively will play a pivotal role in ensuring that advancements in AI create opportunities for workers, rather than acting as barriers to employment.
The Importance of Lifelong Learning in an Evolving Job Market
As the labor market continues to evolve, the concept of lifelong learning has never been more critical. Workers must embrace continuous education and training to adapt to rapidly changing industry trends driven by technological advancements. The increasing prevalence of AI in various sectors calls for employees to develop new skills and competencies that align with the demands of a digitally enhanced economy. Those who invest in their professional development are more likely to remain competitive and relevant in the job market, thereby reducing their risk of job displacement.
Educational institutions, policymakers, and organizations all play significant roles in fostering a culture of lifelong learning. Programs that focus on reskilling and upskilling should be prioritized to help individuals transition seamlessly between roles and industries. As the average job duration decreases and the speed of technological change accelerates, the ability to learn and adapt will undoubtedly be a critical factor determining success in the future workforce. Creating pathways for continued learning will empower individuals to harness the benefits of AI while contributing to a resilient and adaptable labor market.
Understanding Occupational Churn in the Age of AI
Occupational churn refers to the dynamic changes within the labor market, highlighting how job stability fluctuates alongside economic and technological developments. The recent data drawn from extensive research reveals that the rate of occupational churn has seen significant shifts, particularly with the introduction of AI. Understanding these patterns is essential for both employees and employers, as they navigate the complexities of a modern job market shaped by innovation. To mitigate the effects of job volatility, strategies that emphasize flexibility and adaptability will become increasingly important.
Additionally, acknowledging the rate of occupational churn will help policymakers address the challenges faced by workers in transitioning between jobs. With the expansion of sectors focused on AI and technology, career paths may diverge significantly from traditional routes, necessitating a reevaluation of career preparedness and training programs. By recognizing the implications of occupational churn in the workplace, stakeholders can work collectively to create a more resilient labor market that accommodates changes and fosters career mobility.
Future Outlook: Preparing for the Next Wave of Jobs
As we look ahead, it’s crucial to prepare for the next wave of job opportunities that AI and advancements in technology will inevitably bring. While current trends show both growth and decline across various sectors, the ability to embrace change will be paramount in navigating the future labor market landscape. Employers must proactively identify areas of expansion, particularly in high-skilled STEM jobs, and align their workforce development programs accordingly. A strategic approach to workforce planning will ensure that organizations are equipped to meet the evolving needs of the economy.
Furthermore, workers must stay informed about emerging industries and skills that are poised for growth in the coming years. By prioritizing continuous education and training, individuals can position themselves favorably in a competitive environment influenced by technological advancements. Addressing barriers to entry in high-demand fields is essential for creating a diverse talent pool that can thrive in the future job market. Preparing for these changes collaboratively will enable both workers and organizations to harness new opportunities while successfully navigating the challenges presented by a rapidly changing landscape.
AI-Driven Workforce Transformation: Navigating the Challenges Ahead
As AI continues to reshape the workforce, it presents both exciting opportunities and formidable challenges. Companies are already experiencing the impact of AI technologies on job roles and employee dynamics, leading to significant changes in workplace structure and expectations. In light of these developments, it is vital for organizations to create robust support systems to help employees navigate the transition. This involves providing not only training programs but also mental and emotional support to address concerns surrounding job security and workplace adaptation.
Moreover, engaging in conversations about the ethical implications of AI usage in the labor market will be vital as we move forward. Companies should prioritize transparency in how they utilize AI to ensure that workers feel secure and valued in their positions. Fostering a human-centered approach to AI implementation will help mitigate potential backlash while emphasizing the complementary role of technology in enhancing productivity and efficiency. Ultimately, navigating the challenges ahead will require collaborative efforts from all stakeholders to cultivate a workforce that is ready to thrive in an AI-infused era.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the labor market in the United States?
AI is significantly impacting the U.S. labor market, as highlighted by recent studies showing a rise in occupational churn. This indicates that artificial intelligence is facilitating job transformation and creating demand for skills in emerging sectors, especially in STEM fields.
What are the job market trends associated with AI in the workforce?
Recent job market trends indicate a polarization where high-skill, high-paying jobs are expanding while low-wage jobs are declining. Artificial intelligence is accelerating this trend as demand for technical roles increases, reshaping the occupation landscape.
What is occupational churn and how does it relate to AI and technology labor disruption?
Occupational churn refers to the rate at which workers move between jobs or industries. AI and technology have been central to recent labor disruptions, altering employment stability and prompting shifts in job demands across various sectors.
Is there evidence of STEM job growth due to AI technologies in the labor market?
Yes, there is substantial STEM job growth linked to AI technologies. From 2010 to 2024, the share of jobs in science, technology, engineering, and math has risen significantly, indicating that AI is driving the demand for specialized skills in these fields.
What are the implications of AI for future job positions in the labor market?
AI is likely to lead to a restructuring of job positions, with some roles being automated while others requiring more advanced technical skills. Workers must adapt by upskilling to meet new job demands facilitated by AI advancements.
How has AI changed the employment landscape in retail and service jobs?
AI has significantly disrupted the retail and service sectors, contributing to a decline in traditional roles like retail sales, which fell by 25% between 2013 and 2023. This shift illustrates the growing trend toward e-commerce and automation in customer service.
Will AI replace many jobs in the labor market, and what might that mean for workers?
While AI may displace some jobs, it is also expected to create new opportunities that require advanced skills. Workers will need to adapt through continuous learning and skills development to remain relevant in an AI-driven labor market.
What role do economists attribute to AI in shaping job market trends over the last century?
Economists attribute significant changes in job market trends over the past century to AI and other breakthrough technologies. Their research indicates that while there was historical stability, recent rapid changes signal a new era where AI is a major force shaping labor dynamics.
How should workers prepare for the future job market impacted by AI?
Workers should focus on continuous education and upskilling, especially in technical and adaptable roles, to prepare for the job market changes influenced by AI and automation.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Occupational Churn | The study covers 124 years of U.S. Census data revealing that while there was a stable period from 1990 to 2017, significant changes have emerged post-2019, predominantly attributed to AI. |
| Historical Context | The research highlights past technological disruptions and identifies AI as a potential breakthrough technology affecting job markets akin to previous innovations like electricity and keyboards. |
| Job Polarization Trends | Initially, a downward slope within labor markets occurred leading to growth in low-paid jobs; however, a turnaround has seen expansion in high-paid occupations since the late 2010s. |
| STEM Job Growth | An increase in STEM jobs from 6.5% in 2010 to almost 10% by 2024 indicates a significant rise in technical fields, supported by investment in AI and technology. |
| Impact on Low-Paid Jobs | There has been stagnation and decline in low-paid service jobs; positions have sharply declined since 2019, likely impacted by various economic factors including AI. |
| Retail Sales Positions Decline | Between 2013 and 2023, retail sales jobs dropped by 25%, influenced by advancements in e-commerce and AI technology. |
| Future Implications of AI | AI is leading to shifts in job expectations and productivity increases, yet poses risks for displacement among the workforce if technological acumen is not kept up. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is already evident, with recent studies highlighting how artificial intelligence is reshaping various job sectors. From significant declines in low-paid positions, particularly in retail, to notable growth in STEM jobs, the landscape of employment is rapidly evolving. Experts warn of potential job displacement as AI technologies become more ingrained in workplace processes, leading to heightened expectations on knowledge workers. This ongoing transformation not only empowers the workforce but also necessitates adaptation and upskilling to thrive in an increasingly automated environment.